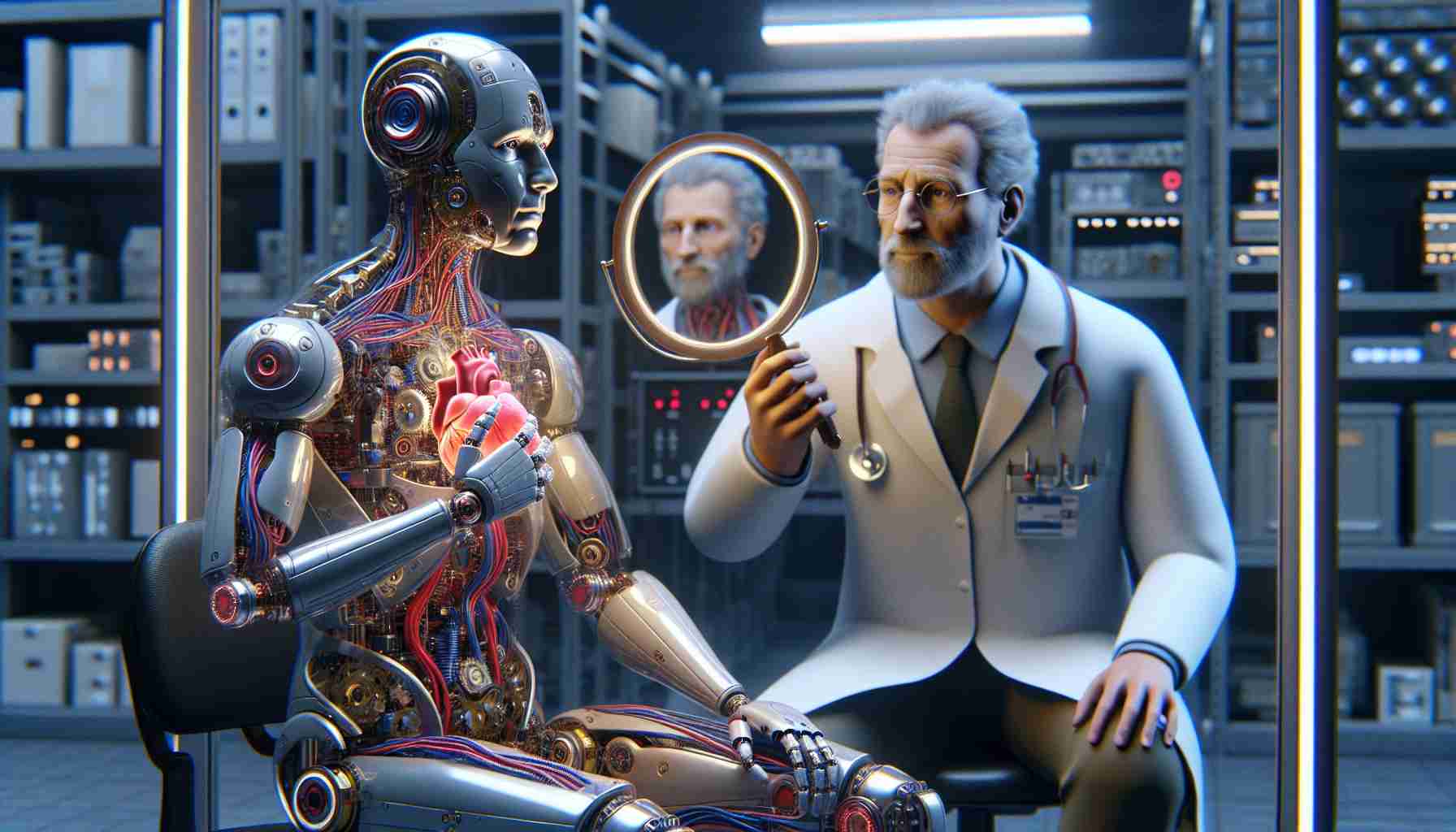
In an exciting blend of technology and psychology, fresh research reveals how robots can be utilized to investigate the intricate human concept of self-identity. Scientists propose that by simulating aspects of self-related processes, robots can provide profound insights into how we perceive our own existence. These robotic models are not just mere machines; they embody complex behavioral mechanisms resembling agency and body ownership, aspects fundamental to the human experience of self.
Moreover, the interdisciplinary collaboration among cognitive robotics, psychology, and psychiatry opens avenues to examine conditions that disrupt self-perception, such as autism or schizophrenia. The team believes that by programming robots to emulate self-related processes, we can better comprehend the development and intricacies of the sense of self.
Under experiments, humans often perceive these robots as social beings capable of agency, leading researchers to question the empathetic connections we forge with them. This newfound understanding invites exploration into how human-like characteristics in robots can influence our interactions and emotional responses.
The study emphasizes the potential of robots to serve as experimental tools, allowing researchers to investigate the self beyond mere biological confines. As this field evolves, it promises to reveal not only the essence of human identity but also how we might recreate or reinterpret it through artificial means, marking a pivotal shift in understanding consciousness.
Unraveling Identity: How Robots Can Teach Us About Ourselves
The intersection of robotics and psychology has unveiled fascinating prospects for understanding human identity through the lens of artificial intelligence. Recent advances reveal that robots, modeled to mirror human self-related processes, have the potential to provide insights into our own sense of being. What are the implications of these findings on our understanding of self-identity?
Key Questions and Answers
1. How do robots simulate self-related processes?
Robots can be equipped with algorithms that enable them to recognize and respond to their own states, just as humans do. By simulating aspects of self-awareness, such as recognizing their physical boundaries and responding to social cues, these robots create a platform through which researchers can examine the components of human identity.
2. What ethical considerations arise from creating self-aware robots?
The advent of robots capable of displaying human-like characteristics raises ethical dilemmas concerning autonomy and rights. Should robots that exhibit signs of self-awareness be afforded certain rights, or are they fundamentally different from humans? These questions challenge our preconceived notions of identity and the moral landscape surrounding AI.
3. Can robots assist in empathy development?
While robots can simulate social interactions, whether they promote genuine empathy in humans is contentious. Some researchers suggest that interaction with empathetic robots might enhance emotional intelligence, whereas others argue that it could lead to an artificial understanding of social connections.
Challenges and Controversies
One of the major challenges in utilizing robots to understand identity is the distinction between genuine human experiences and those simulated by machines. There is an ongoing debate about whether robots can truly replicate human processes or if they merely mimic behaviors without understanding underlying emotions or experiences.
Additionally, there are concerns regarding mental health implications. While robots can serve as therapeutic tools for individuals with conditions like autism or anxiety, reliance on artificial companions could detract from human social interactions, further complicating relational dynamics.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
– Research Flexibility: Robots can be programmed to exhibit various traits and behaviors, providing researchers with flexible models to study complex topics such as self-identity and social behavior.
– Therapeutic Potential: As therapeutic companions, robots may offer safe environments for individuals to practice social skills and explore their identities without the fear of judgment.
– Empirical Experimentation: The ability to observe consistent robotic behaviors allows for empirical studies that might reveal patterns in identity formation and social interaction that are difficult to isolate in human subjects.
Disadvantages:
– Emotional Detachment: Engaging with robots may lead to desensitization to real emotional connections with people, posing a risk to mental health and social skills.
– Dependence: There is a potential for individuals to become overly reliant on robotic interaction as a substitute for real human relationships.
– Philosophical Implications: The evolution of robot-human relationships could blur the lines of self-identity and consciousness, raising questions about what it truly means to be “self-aware.”
As research continues to unfold in this fascinating domain, it becomes clear that the study of robots and their relation to human identity is not merely about technology. It challenges us to explore essential questions about consciousness, empathy, and the very fabric of human connection.
To learn more about related topics, you can explore these resources: Science Daily and Nature.