Advancements at Oak Ridge National Laboratory
At Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), a groundbreaking robot has been introduced that changes the game for environmental data collection. This innovative robot is designed to autonomously collect soil samples, paving the way for more efficient research on plant-soil interactions.
The need for improved understanding in biomass productivity and carbon cycling has led scientists to create this robotic system, which captures critical data much faster than traditional methods. Current estimates suggest that soil stores an astonishing amount of carbon—trillions of tons—three times that of the atmosphere—underscoring the significance of accurate sampling.
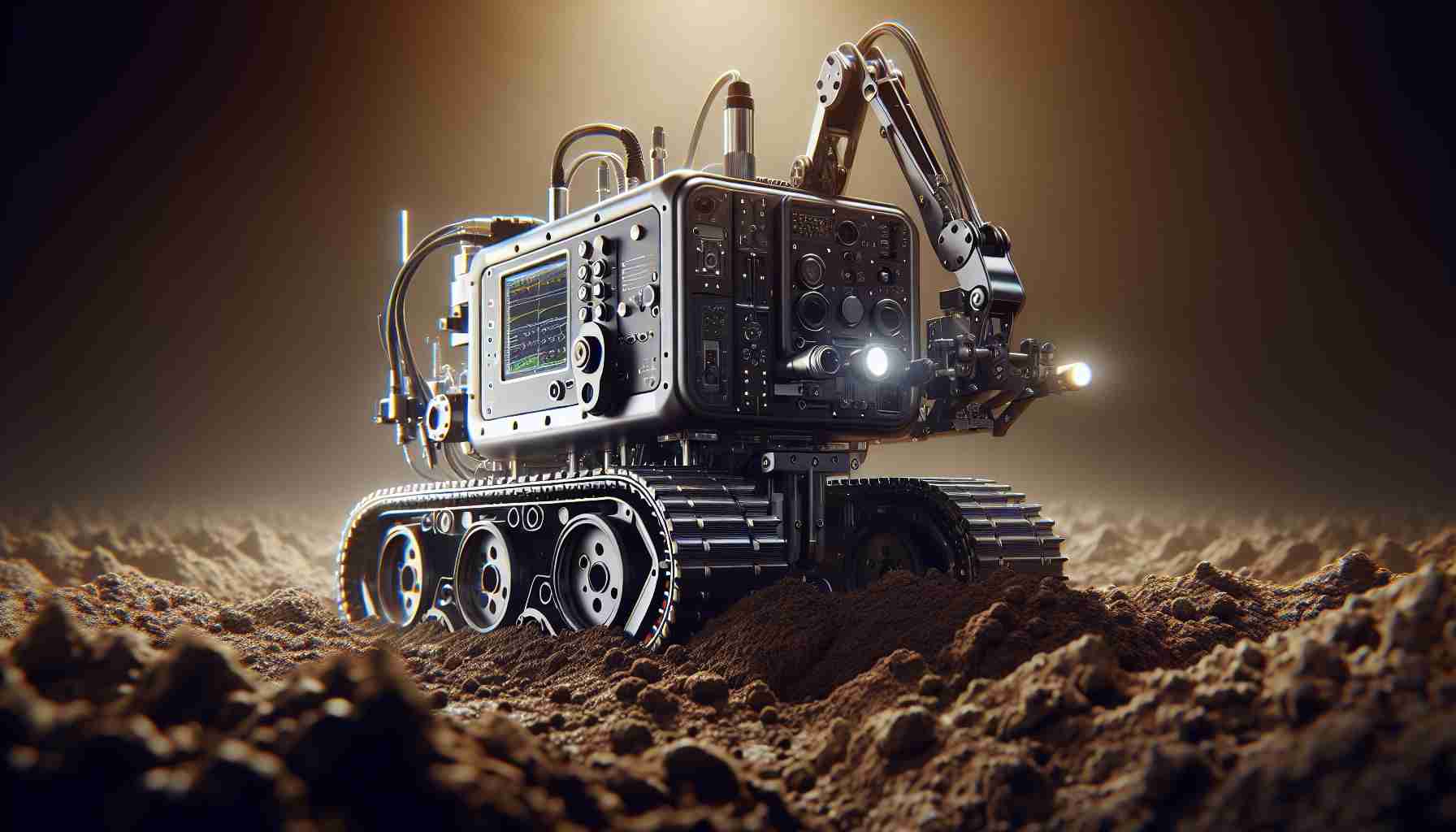
Known as the SMART Plant F-Series, the robot navigates using GPS and laser sensing technologies, allowing it to collect soil samples with minimal disruption to surrounding plants. Researchers can now effortlessly gather vital information on soil characteristics and plant productivity, enhancing connections between laboratory findings and field conditions.
The robot works in unison with ORNL’s Advanced Plant Phenotyping Laboratory, which examines the relationships between various plant traits and environmental factors. By deploying such autonomous systems, ORNL aims to develop an interconnected network of robots that provide real-time data from diverse ecosystems, ultimately aiding smarter agricultural practices.
This revolutionary project signifies a giant leap forward in ecological research, promising to yield richer insights into the manifold relationships within our environment.
Revolutionizing Soil Research: The Future of Environmental Data Collection
Advancements at Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is making significant strides in environmental research with the introduction of its cutting-edge SMART Plant F-Series robot. This autonomous robot is poised to transform the field of soil sampling by enabling rapid and efficient collection of environmental data critical to understanding plant-soil interactions.
# Overview of the SMART Plant F-Series
The SMART Plant F-Series robot is engineered to navigate complex landscapes using state-of-the-art GPS and laser sensing technologies. By autonomously collecting soil samples while minimizing disruption to surrounding vegetation, it enhances the quality and quantity of data researchers can obtain. This capability allows scientists to gather information on soil characteristics and plant productivity at an unprecedented pace.
Key Features:
– Autonomous Navigation: Utilizes GPS and laser sensors for precise movement and sampling.
– Minimal Disruption: Collects samples without harming nearby plants.
– Data Collection Efficiency: Transforms traditional sampling methods by speeding up data retrieval.
# Use Cases and Applications
The implementation of the SMART Plant F-Series is crucial for several research areas:
– Biomass Productivity: Facilitates studies aimed at understanding how various factors contribute to plant growth and resource allocation.
– Carbon Cycling: Enhances knowledge of soil carbon storage, which is estimated to hold three times more carbon than the atmosphere. This understanding is vital for climate change research and mitigation strategies.
– Agricultural Practices: By connecting laboratory findings with real-field data, the robot aims to inform smarter agricultural techniques that could improve sustainability.
# Pros and Cons
Pros:
– Increases efficiency and speed of soil sampling.
– Provides real-time data that improves research accuracy.
– Enhances the understanding of ecological interactions, benefiting agriculture and environment conservation.
Cons:
– Initial development and deployment costs may be high.
– Potential dependency on technology could overlook traditional methods.
# Limitations
While the innovations brought by the SMART Plant F-Series are promising, there are certain limitations to consider:
– Environmental Constraints: Not every ecosystem is suited for robotic navigation; rugged or densely vegetated areas may pose challenges.
– Technical Reliability: Ensuring the robot operates flawlessly across varying conditions is essential before widespread deployment.
# Market Trends and Predictions
The emergence of autonomous robots in environmental science, such as the SMART Plant F-Series, reflects a broader trend towards automation in research. As climate change continues to drive research priorities, the demand for efficient data collection methods is expected to grow significantly. Future predictions suggest that the integration of robotic systems in ecological studies will lead to more nuanced insights into environmental processes, paving the way for innovations in sustainability and conservation efforts.
In conclusion, the SMART Plant F-Series robot epitomizes the forefront of technological innovation in environmental research, providing critical tools that can significantly improve our understanding of ecological dynamics. Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s advancements signal a new era in automated environmental data collection, and its implications could extend far beyond research, impacting agricultural practices and climate strategies.
For more information on advancements in robotic technology and environmental science, visit Oak Ridge National Laboratory.