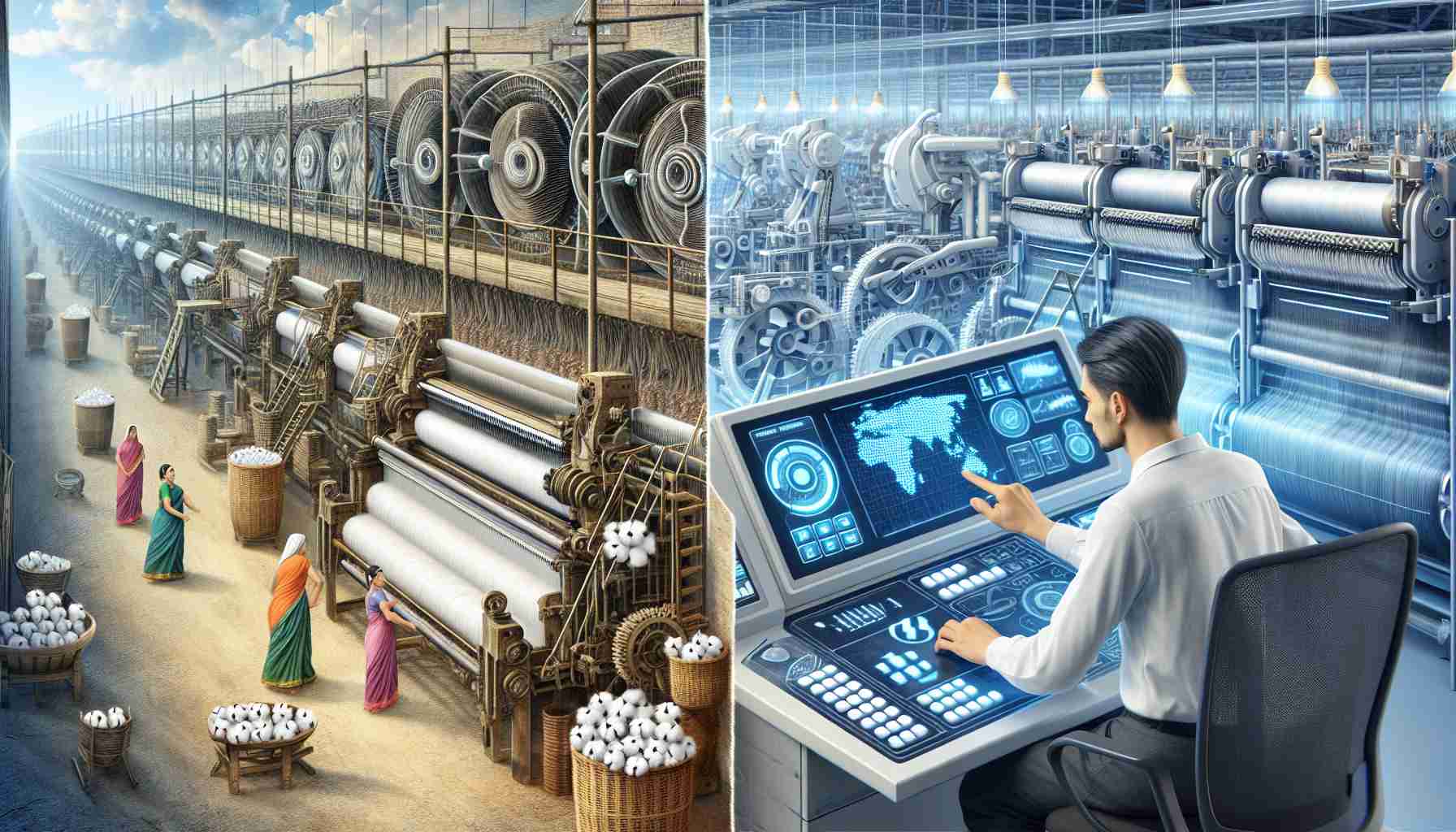
The textile industry is undergoing a transformation as automation and robotics reshape its future, pushing boundaries and introducing innovative practices. With the rise of Industry 4.0, the incorporation of advanced robotic technology is enhancing precision and operational efficiency. Manufacturing processes are now faster, minimizing human error and reducing production time. The implementation of smart machinery and AI systems allows for real-time monitoring, ensuring that high-quality standards are consistently met while improving responsiveness to consumer demands.
Sustainability has also become a core focus for the modern manufacturing landscape. With the increasing adoption of robotics, the reduction of material waste is more achievable than ever. Automated systems meticulously utilize resources, allowing textile manufacturers to make the most of their materials while significantly reducing excess. By automating recycling processes, companies are able to repurpose leftover fabric, contributing positively to both cost control and environmental initiatives.
Further, the accessibility of refurbished machinery allows smaller textile businesses to embrace automation without incurring prohibitive costs. This adoption of second-hand equipment not only supports economic viability but also promotes environmentally responsible practices by extending the lifespan of machinery.
Finally, the trend towards customization is being driven by automation technologies that cater to consumer preferences for unique textiles. Manufacturers can rapidly create distinctive patterns and features, responding promptly to market trends. Such advancements not only meet evolving consumer expectations but also streamline production, confirming that the textile industry’s future is bright and innovative.
Revolutionizing Textiles: How Automation is Changing the Game
The textile industry stands on the brink of a significant transformation, with automation reshaping traditional practices and introducing groundbreaking technologies. While many advancements have been highlighted, several additional factors deserve attention.
What is the emergence of smart textiles?
One of the most exciting developments is the advent of smart textiles, which integrate electronic components such as sensors and actuators directly into fabrics. This technology allows textiles to respond to different stimuli, which opens up new applications in fashion, healthcare, and automotive industries. For instance, garments that can monitor vital signs or adapting to body temperature are on the rise, showcasing how automation reaches beyond mere production efficiency.
How does automation affect labor dynamics?
While automation translates to increased efficiency, it raises critical questions about job displacement. Many workers fear that machines will replace human roles, especially in low-skilled positions. However, the reality is that automation creates opportunities for higher-skilled jobs, especially in programming, maintenance, and oversight of automated systems. Upskilling current employees becomes an essential strategy to address these shifts in labor dynamics.
What are the key challenges in implementing automation?
Despite the advantages, the transition to automated processes is not without challenges. High initial costs for technology adoption can be burdensome for smaller enterprises. Moreover, the integration of automated systems requires significant changes in production processes and workforce skill levels. Resistance to change, particularly from traditional industries accustomed to manual practices, can hinder the pace of adoption.
Are there controversies surrounding automation in textiles?
Automation also raises ethical concerns, particularly around data privacy and security. With the increasing reliance on interconnected machines and AI, manufacturers must ensure robust cybersecurity measures to protect intellectual property and consumer data. There is also a substantial debate surrounding the environmental impact of automation. While on the surface, automation reduces waste, the manufacturing processes for advanced machinery can have a large carbon footprint.
What advantages and disadvantages does automation bring to the textile industry?
Advantages:
1. Increased Efficiency: Automated systems operate continuously, significantly increasing production rates.
2. Improved Quality Control: Machines provide consistent quality, minimizing human errors in production.
3. Customization: Automation enables quick changes to designs based on consumer preferences, allowing for fast fashion cycles.
4. Sustainability: By precisely controlling material usage, automation reduces waste, and processes can be designed for recycling.
Disadvantages:
1. Job Displacement: Automation can lead to significant job losses in low-skilled sectors.
2. High Initial Costs: Small businesses might find it challenging to invest in expensive automated systems.
3. Skills Gap: There is a growing need for workers with technical skills to manage and maintain automated systems.
4. Cybersecurity Risks: Increased reliance on technology makes the sector vulnerable to cyber attacks.
As the textile industry continues on this path of automation, stakeholders must navigate these complex challenges while maximizing the benefits. The integration of competing interests, ethical considerations, and economic constraints will shape the industry’s evolution.
For further exploration of the intersection of automation and textiles, check out ITU’s textile industry initiatives or Textile World’s analysis.