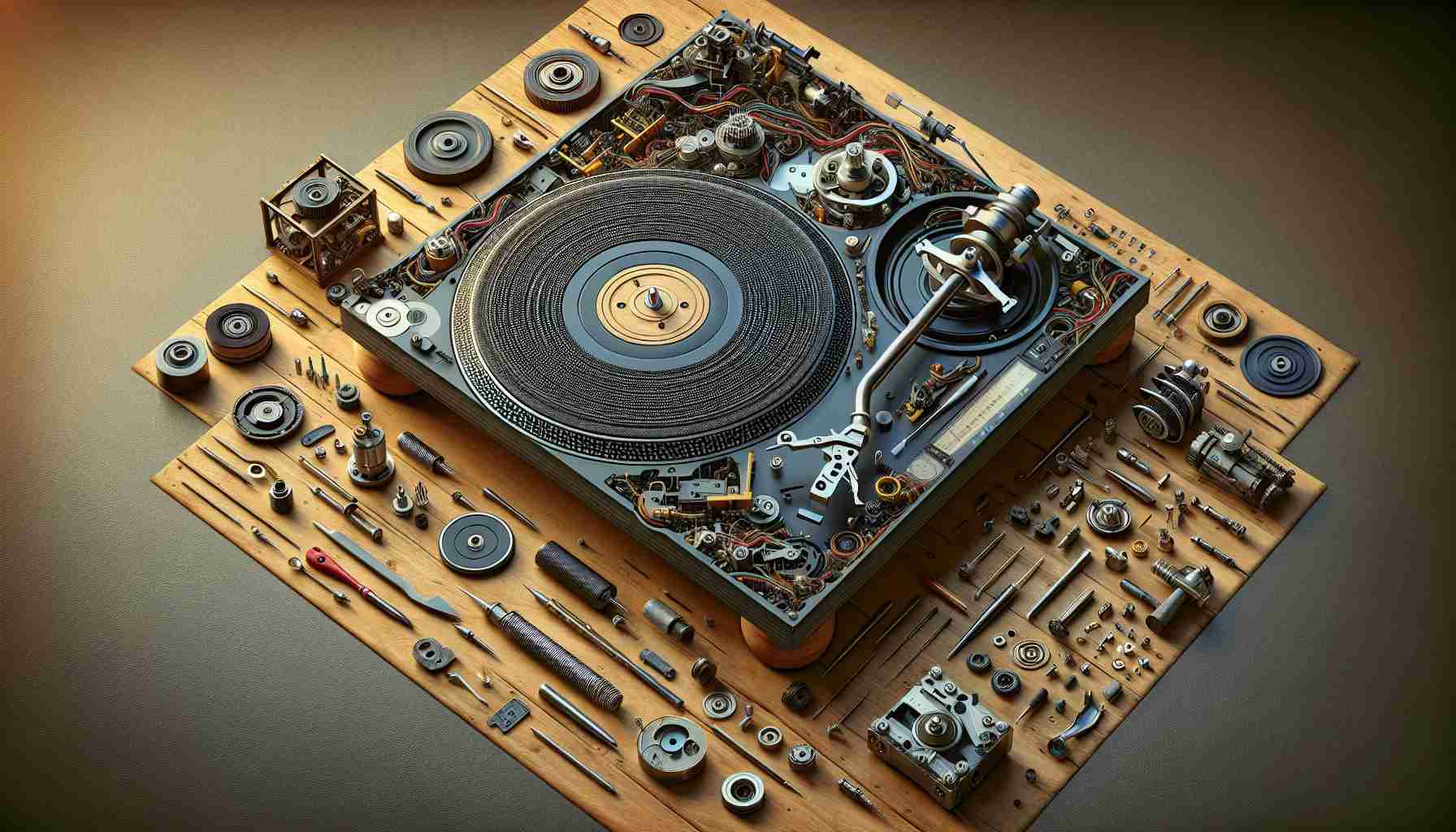
When exploring the world of turntables, it’s essential to understand their key components, which significantly influence sound quality. A typical turntable comprises a solid base known as the plinth, a rotating platter for the record, a motor that drives the rotation, and the tonearm that holds the cartridge. Effective designs offer reinforced structures and sound isolation between these parts to minimize unwanted noise, enhancing the overall listening experience.
Most contemporary turntables feature either a belt drive or a direct drive motor system. Direct drive systems, favored by DJs, enable the platter to spin immediately through a dedicated motor, exemplified by models like the Technics SL1200. Conversely, belt-driven turntables, which prioritize consumer usability, utilize a rubber belt that reduces noise by absorbing motor vibrations.
The cartridge, a small box at the end of the tonearm, contains the stylus which makes contact with the vinyl record. Higher-quality designs allow users to swap cartridges, providing opportunities for improved audio output. A switch for electronic speed adjustment is another useful feature, allowing easy transitions between play speeds without having to manually adjust the belt.
Incorporating onboard preamps can also enhance convenience, making it easier to connect to sound systems. Modern turntables often include additional functionalities such as Bluetooth, USB connections, or even CD players. Prices vary widely, with entry-level options available from about $50, while advanced models suitable for serious audiophiles can exceed $1,000.
Understanding the Anatomy of Turntables: A Deeper Dive
Turntables have made a significant comeback in recent years, appreciated by audiophiles and casual listeners alike. Beyond the basic components of a turntable, a deeper understanding of its anatomy reveals factors that contribute to its performance and user experience.
What Are the Key Components of a Turntable?
While most people are familiar with the platter, tonearm, and cartridge, several lesser-known components also play crucial roles. For instance, the anti-skate mechanism helps maintain the correct tracking of the stylus on the record, thus preventing excessive wear and tear while maintaining sound fidelity. Additionally, some high-end turntables include vibration dampening materials within their plinth, which can significantly improve audio playback by reducing feedback from external sources.
What Are the Modern Variations of Turntables?
In the contemporary market, turntables come in various forms. The evolution has led to innovations such as automatic turntables which can detect the end of a record and lift the tonearm automatically. Portable turntables, designed for mobility, have also gained popularity, appealing to music lovers who enjoy listening on the go. Each of these variations addresses different consumer needs.
Key Challenges in Turntable Use and Maintenance
One of the most pressing challenges for turntable users is stylus maintenance. Over time, the stylus can wear down, affecting sound quality. Users must consider periodic replacement to keep audio performance optimal. Another challenge is the need for precise setup, including correct anti-skating adjustments and tracking force. Many users overlook this step, which can lead to subpar sound quality and potential damage to records.
Controversies in Turntable Design
There remains an ongoing debate regarding the benefits of direct drive versus belt drive systems. Proponents of direct drive systems argue that they offer superior speed stability and low maintenance, which is ideal for DJs. In contrast, advocates of belt-driven systems favor their audio quality, as the belt serves to isolate motor vibrations from the platter, often resulting in clearer sound reproduction. Each type has passionate supporters, making this a nuanced subject in audiophile circles.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Turntables
Advantages:
1. Richness of Sound: Many enthusiasts argue that vinyl provides a warmer, richer sound experience compared to digital formats.
2. Tactile Experience: The physical interactions involved in playing records offer a unique user experience, fostering a deeper connection to the music.
3. Collectibility: Vinyl records are often collectible, adding an element of fun for hobbyists.
Disadvantages:
1. Maintenance: Turntables require regular cleaning and maintenance, including stylus replacement and record cleaning.
2. Space Requirements: Full-sized turntables and record collections can take up significant space, which can be a drawback for those in smaller living environments.
3. Initial Investment: High-quality turntables can be costly, and audiophiles often spend significant sums on ancillary equipment, like speakers and amplifiers.
Conclusion
Understanding the anatomy and functionality of turntables not only enhances the listening experience but also helps buyers make informed decisions. Whether one is an audiophile seeking high fidelity or a casual listener enjoying nostalgia, knowledge of turntable components, maintenance, and audio output is essential.
For more information and resources on turntables, you can visit Turntable Lab.