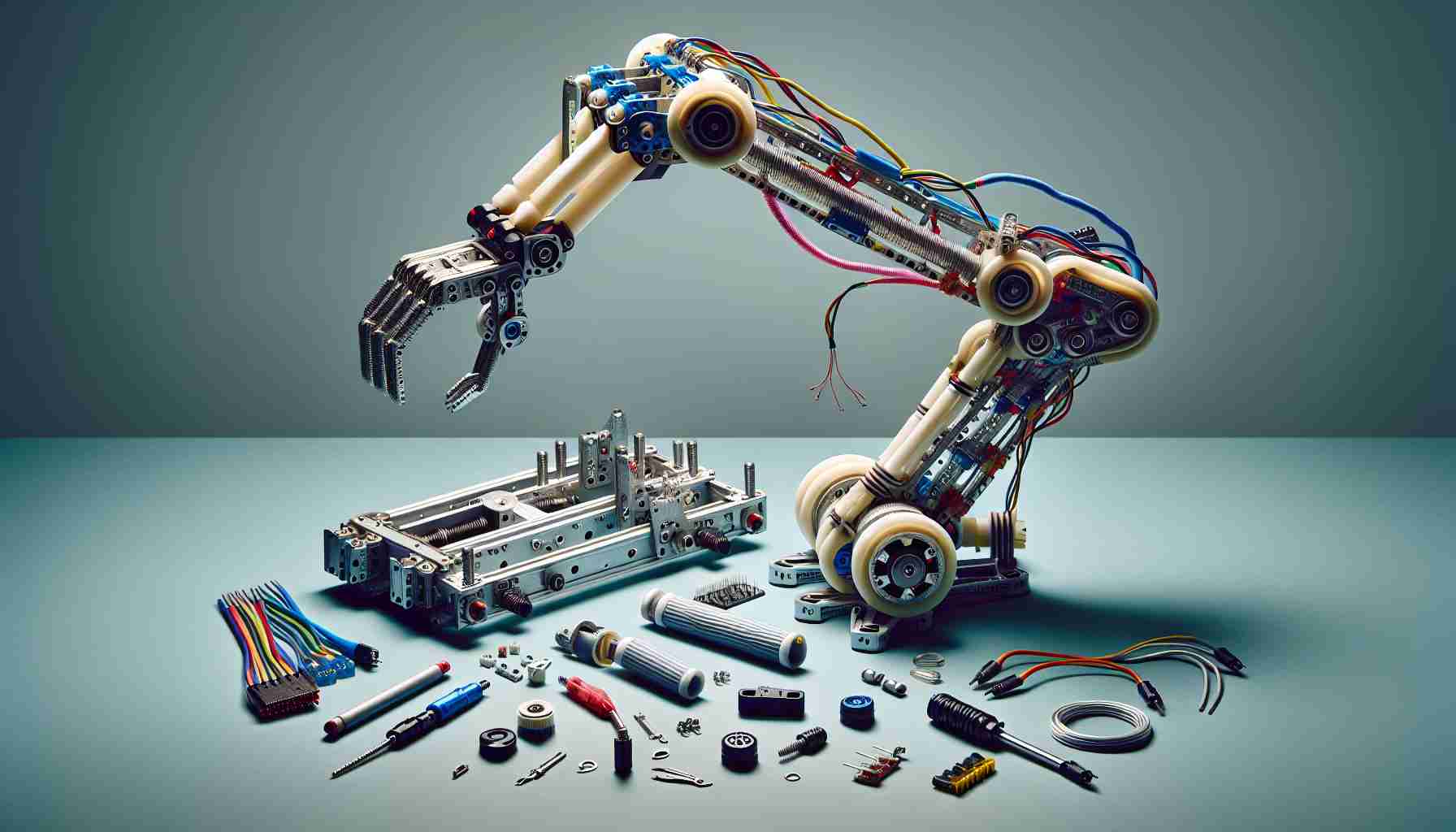
If you’re eager to dive into the world of robotics while having a blast, a practical project might be just what you need! Imagine building your very own robotic arm that not only teaches you about engineering, but also allows you to play and experiment with technology.
Enter Pedro 2.0, a straightforward and engaging robot arm designed specifically for educational purposes in STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics). This creation is perfect for anyone, regardless of age, who has a curiosity for building and programming.
The assembly of Pedro 2.0 uses components that can easily be found globally, including SG90 servo motors, ball bearings, and an Arduino board that coordinates its functions. Moreover, with the inclusion of an NRF24L01 module, you’re set up for wireless control, adding an exciting twist to the experience. Best of all, the major mechanical parts can be downloaded and printed on any standard 3D printer.
This project serves as an excellent introduction to the fascinating realm of robotics. It provides a foundational understanding from which you can branch out into more complex designs or even dream up your own creations. The possibilities are limitless, paving the way for endless exploration and innovation!
Unlock Your Inner Engineer: Create This Fun DIY Robot Arm!
If you’re looking for an engaging way to learn about robotics and engineering, building your own DIY robot arm can be both an exhilarating and educational experience. Not only does it allow you to explore fundamental mechanical and programming concepts, but it also offers opportunities to enhance your creative skills.
Understanding Robot Arm Mechanics
Before delving into assembly, it’s essential to grasp the basic mechanics behind robotic arms. These devices mimic the movement of a human arm through joints and segments, controlled by motors that serve as muscles. Each joint’s movement is coordinated to perform tasks, providing insights into kinematics—the study of motion without considering forces.
What Makes Pedro 2.0 Stand Out?
Pedro 2.0 is designed for enthusiasts ranging from beginners to advanced makers. Its components—like SG90 servo motors and an Arduino board—standardize the build process, making it relatively easy and cost-effective. The ability to wirelessly control the arm using an NRF24L01 module not only enhances interactivity but also invites users to delve into concepts of wireless technology.
Key Questions About Building a DIY Robot Arm
1. What components are necessary for building a robot arm?
– Key components include servo motors, an Arduino board, 3D printed parts, power supply, and optional wireless modules for remote control.
2. Are there any prerequisites for building a robot arm?
– A basic understanding of electronics and programming can be beneficial, especially in using Arduino. However, many tutorials cater to absolute beginners.
3. How long does it typically take to build a robot arm?
– The assembly can take anywhere from a few hours to several days depending on the complexity of the design and your experience level.
Challenges and Controversies
While engaging in DIY robot projects is rewarding, there are challenges to consider. One of the major issues is the accessibility of components. Although many parts can be sourced globally, shipping delays and availability might hinder immediate progress. Additionally, there’s often a steep learning curve associated with programming and electronics, which may deter some beginners.
Another controversy in the DIY robotics community is the debate between using pre-fabricated kits versus sourcing individual components. Kits streamline the building process but can limit creativity, while sourcing individual parts can provide a more customized and fulfilling experience.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
– Educational Value: Enhances understanding of engineering principles, electronics, and programming.
– Skill Development: Promotes critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity.
– Customization: Allows for unique designs based on personal preferences and capabilities.
Disadvantages:
– Time-Consuming: Building and troubleshooting can take significant time.
– Cost: While many components are affordable, the costs can add up, especially if mistakes are made.
– Frustration Level: Beginners may face challenges that could lead to frustration if guidance is limited.
In summary, creating a DIY robot arm like Pedro 2.0 is a fantastic way to unlock your inner engineer. The potential for exploration and innovation is immense, and with the right mindset, the journey can be just as rewarding as the end product.
For further exploration into robotics, check out Robotics Online for resources and community support.